Understanding Audio Equipment: A Comprehensive Overview
Audio equipment plays a crucial role in delivering high-quality sound for various applications, from casual listening to professional audio production. Whether you’re a music enthusiast, a home theater aficionado, or a sound engineer, understanding the different types of audio equipment can greatly enhance your experience.
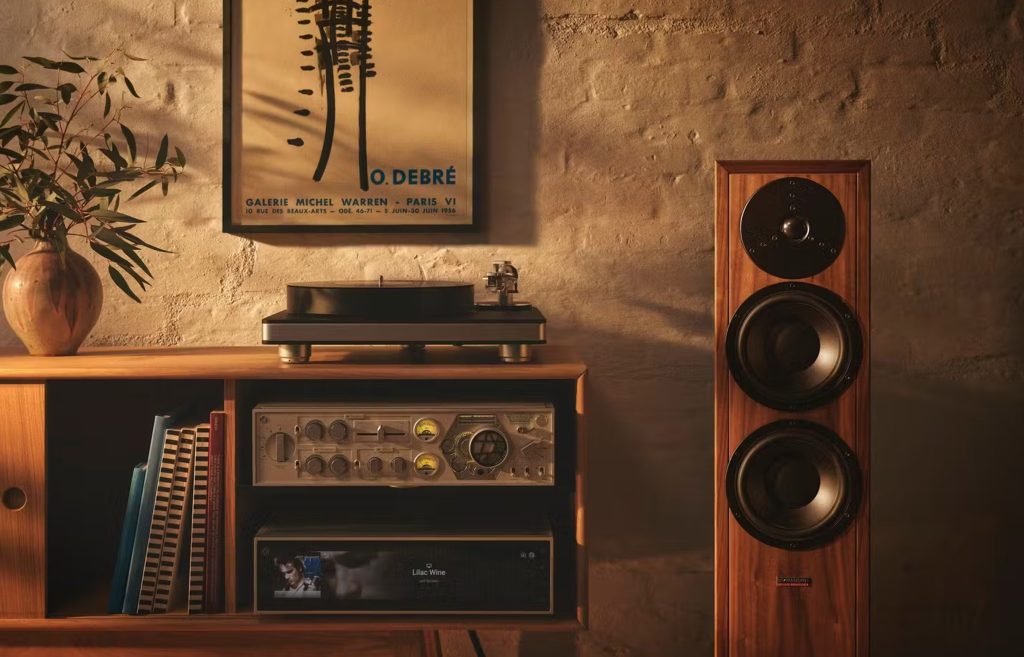

1. Speakers
Speakers are fundamental to any audio setup. They convert electrical signals into sound waves, and their quality significantly impacts the listening experience. There are several types of speakers, including:
- Bookshelf Speakers: Compact and versatile, ideal for small to medium-sized rooms.
- Floor-standing Speakers: Larger and more powerful, suitable for bigger spaces.
- Subwoofers: Designed to handle low-frequency sounds, providing depth and richness to music and movies.

2. Amplifiers
Amplifiers boost the audio signal from your source device to a level that can drive the speakers. They come in various forms:
- Integrated Amplifiers: Combine a preamplifier and a power amplifier in one unit, making them a convenient all-in-one solution.
- Power Amplifiers: Focus solely on amplifying the signal, often used in conjunction with a separate preamplifier.
- Tube Amplifiers: Use vacuum tubes to amplify the signal, offering a warm and distinctive sound quality favored by audiophiles.

3. Receivers
Audio receivers serve as the central hub for managing and processing audio signals. They combine an amplifier with a tuner and various input/output options. Modern receivers often include additional features such as:
- Surround Sound Processing: For immersive audio experiences in home theaters.
- Streaming Capabilities: Allowing direct playback from online services.
- Multiple Inputs: To connect various audio and video sources.
4. Headphones
Headphones provide a personal listening experience. They come in several styles:
- Over-Ear Headphones: Enclose the ears completely, offering superior sound quality and noise isolation.
- On-Ear Headphones: Rest on the ears, providing a more compact design.
- In-Ear Monitors: Fit inside the ear canal, ideal for portability and noise isolation.
5. Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs)
DACs convert digital audio signals into analog signals that can be amplified and played through speakers or headphones. High-quality DACs can significantly improve sound clarity and detail.
6. Microphones
Microphones capture audio signals and convert them into electrical signals. They vary based on their use:
- Dynamic Microphones: Durable and versatile, suitable for live performances and loud sound sources.
- Condenser Microphones: Sensitive and accurate, ideal for studio recording and capturing subtle details.
Conclusion
Choosing the right audio equipment depends on your needs and preferences. Whether you’re setting up a home theater system, creating a music studio, or simply enhancing your listening experience, understanding the roles and functions of different audio components can help you make informed decisions and enjoy superior sound quality.